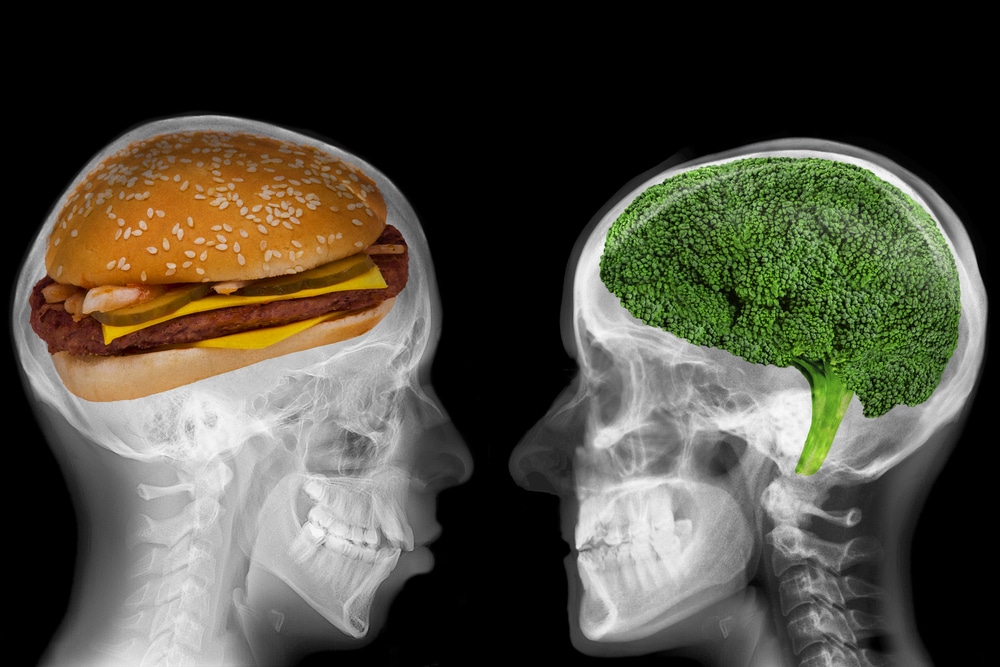
You are what you eat. It’s a cliché phrase that most of us have heard but probably have not put much thought into. We know that certain types of diets can lead to health problems, such as obesity, diabetes, and high cholesterol, but did you know that what you eat can also have an impact …